In this post you will learn how to check whether a particular worksheet exists inside a workbook. There are few different ways to check it. I will show you two methods here. In both methods we are going to use the name of the worksheet to identify the existence. First method will use a string comparison function and the second method will use an error handling technique.
Check if sheet exists - Method 1
Check if sheet exists - Method 2
Check if sheet exists and then delete using VBA
If sheet does not exist then skip
Here is a sample workbook which contains a few worksheets.
Method 1
This workbook has three worksheets. Names of the worksheets are “Input”, “Tmp” and “Output”. Assume we want to check if sheet “Tmp” exists inside this workbook. Here is the first function you can use to check that.
Dim WS As Worksheet
For Each WS In WB.Worksheets
If StrComp(SheetName, WS.Name, vbTextCompare) = 0 Then
IsSheetExist = True
Exit Function
End If
Next WS
End Function
And this is how you can call this function from a subroutine.
Dim WB_Data As Workbook
Dim Result As Boolean
Set WB_Data = ActiveWorkbook
Result = IsSheetExist(WB_Data, "Tmp")
MsgBox Result
End Sub
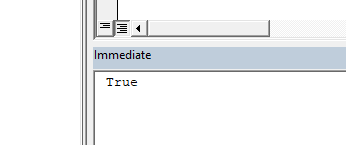
If you run the macro when the “Tmp” sheet is available inside the workbook then you will see this message box.
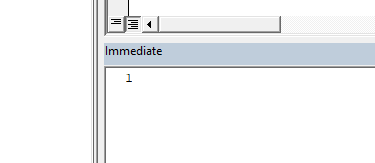
This is the result you will see when there is no “Tmp” sheet.
Below is the explanation for the first function.
This function has two parameters. And the data type of the return value is boolean.
Function uses a For Each Next statement to iterate through the sheets of the given workbook.
Next WS
StrComp function is used to compare the given name with each and every sheet name.
End If
Learn more about StrComp function
If a match is found then the function will return the value “True” and exit.
If StrComp(SheetName, WS.Name, vbTextCompare) = 0 Then
IsSheetExist = True
Exit Function
End If
Next WS
If the function is unable to find a matching sheet name inside the For Each Next statement, the code will be executed until the “End Function” line. Then the function will return false as the default value of a VBA function is false.
Method 2
In this method we are going to use error handling techniques to check if a sheet exists in a workbook. Below is the complete code for the second function.
Dim WS As Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(SheetName)
If Err <> 0 Then
IsSheetExist = False
Else
IsSheetExist = True
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End Function
You can call this function from a subroutine same as we did above for the first function.
If there is no sheet named as SheetName then the above line will generate an error like this.
To prevent that run-time error “On Error Resume Next” statement is used before that line. So the program will execute the next lines without raising the error. Next the below part will identify whether there is an error or not and output return value for the function accordingly.
IsSheetExist = False
Else
IsSheetExist = True
End If
In VBA we use <> for not equal. It is the opposite of = symbol. So Err<>0 means error is not equal to zero. So there is an error. Then we can decide that the error occurred due to there not being such a sheet. So we return false for the function. Else we can return true.
So we learnt two different ways to check if a sheet exists inside a workbook. Sometimes we have to take some other actions after checking the existence of a particular sheet. Now let’s look at a few examples where we need to take another action after checking the existence of a sheet.
Check if sheet exists and delete using VBA
Sometimes you may need to check whether a particular sheet exists and then delete it if it exists. Here is one way to do it.
Dim WS As Worksheet
For Each WS In WB.Worksheets
If StrComp(SheetName, WS.Name, vbTextCompare) = 0 Then
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
WS.Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Exit Function
End If
Next WS
End Function
You can call the above function inside a subroutine like this.
Dim WB_Data As Workbook
Set WB_Data = ActiveWorkbook
Call DeleteIfSheetExist(WB_Data, "Tmp")
End Sub
You might wonder why you need to check the existence of the sheet. You can delete the sheet straight away. Then if an error raises when there is no sheet with that name you can use “On Error Resume Next” to proceed without any interruption. Actually you can delete the sheet without checking its existence. But the problem is that errors can be raised due to different other reasons. For example, an error can be raised if you try to delete a sheet of a protected workbook. However there is a turnaround for that as well. You can identify the reason for the runtime error using the err number and then develop the code accordingly.
If sheet does not exist skip
Sometimes you may need to skip some processes if a sheet does not exist. For an example assume you want to call another subroutine if a sheet exists and skip if it doesn’t.
Dim WB As Workbook
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim SheetName As String
Set WB = ActiveWorkbook
SheetName = "Tmp"
On Error Resume Next
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(SheetName)
If Err <> 0 Then
'Do nothing
Else
On Error GoTo 0
Call OtherSub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
Also you can shorten the above if statement section like this as well.
Dim WB As Workbook
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim SheetName As String
Set WB = ActiveWorkbook
SheetName = "Tmp"
On Error Resume Next
Set WS = WB.Worksheets(SheetName)
If Err = 0 Then
On Error GoTo 0
Call OtherSub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub