In this post you will learn about different ways to select all cells of a worksheet using VBA. When developing VBA macros you may need the VBA program to select all cells of a worksheet. For an example you might need to select all cells before printing the Excel sheet. There are many ways to select all cells of an Excel worksheet using VBA. In this lesson you will learn four different ways to select all cells of an Excel sheet.
Select all cells using Cells.Select Method
Select all cells using UsedRange property
Select all cells using last row and column numbers
Select all cells using CurrentRegion property
Cells.Select Method
This is the simplest way to select all the cells of an Excel worksheet using VBA. If you want to select all the cells of the activesheet then you can use the below code to do that.
ActiveSheet.Cells.Select
End Sub
However keep in mind that this method will select all cells of the worksheet including the empty cells.
Sometimes you may need to select all cells of a specific sheet of a workbook which contains multiple worksheets. Then you can refer to that specific sheet by its name. If the name of the sheet is “Data” then you can modify the above VBA macro as follows.
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Worksheets("Data")
WS.Activate
WS.Cells.Select
End Sub
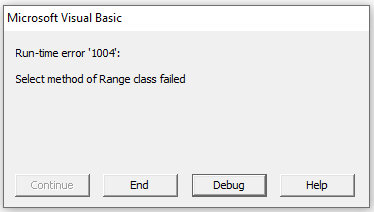
Note that it is important to use the Worksheet.Activate method before selecting all cells. Because the VBA program can’t select cells of a worksheet which is not active. Program will throw an error if you try to select cells of a worksheet which is not active.
UsedRange Method
Above macros select all the cells of the worksheet. So VBA programs select cells even beyond the last row and column having data. But what if you want to select all the cells only inside the range you have used? For that you can use Worksheet.UsedRange property.
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Worksheets("Data")
WS.Activate
WS.UsedRange.Select
End Sub
Above VBA code will select all the cells inside the range you have used.
Select all cells using last row and column numbers
Also there is an alternative way to do this using VBA. First we can find the row number of the bottom most cell having data. Next we can find the column number of the rightmost cell having data. Then we can select the complete range from cell A1 to cell with those last row and column numbers using VBA. Here is how we can do it.
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim WS_LastRow As Long
Dim WS_LastColumn As Long
Dim MyRange As Range
Set WS = Worksheets("Data")
WS_LastRow = WS.Cells.Find("*", [A1], , , xlByRows, xlPrevious).Row
WS_LastColumn = WS.Cells.Find("*", [A1], , , xlByColumns, xlPrevious).Column
Set MyRange = WS.Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(WS_LastRow, WS_LastColumn))
WS.Activate
MyRange.Select
End Sub
There is one difference between those last two methods. If you use the last row and column numbers method, the range will be selected from cell A1. But if you use the UsedRange property then the range will be started from the first cell with the data. However you can also modify the last row and column numbers macro to get the same result as the Worksheet.UsedRange property method. But it will be a little more complicated.
Using CurrentRegion Property
We can also use the Range.CurrentRegion property to select all cells of an Excel worksheet. We can easily do that by making a slight change to the UsedRange method. Here is how we can select all cells using the CurrentRegion property.
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Worksheets("Data")
WS.Activate
WS.Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Select
End Sub
However there is one limitation in this method. If you have empty rows in your worksheet, then the VBA program will select cells only upto that row.