In this lesson you will learn how to find the style number of an Excel chart using VBA. Let’s consider this sample Excel sheet. This Excel sheet lists the number of sales for a few different items. Then an Excel chart has been used to visualize the sales of each item.
Now let’s see how we can find the style number of this Excel chart using VBA. I will show you how to find the style number of an active chart and of a chart by its name. In the first example you will be able to find the style number of a selected chart.
Find style number of an active chart using VBA
In this example we are going to find the style number of an active chart. To find the style number from this method, first click on the chart you want to find the style number of.
Then run this simple subroutine.
MsgBox ActiveChart.ChartStyle
End Sub
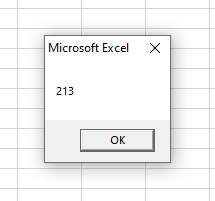
This is the result obtained from the subroutine.
Find the style number of a chart by its name using VBA
From the previous subroutine we were able to get the style number of an active chart. You may know that each chart of a worksheet has a name. So in this next VBA macro we are going to find the style number of an Excel chart by its name. Remember that these names are not unique. Because users can create multiple charts with the same name.
Don’t know how to find the name of a chart? Check this post.
Find the name of a chart in Excel
Now let’s look at how to find the style number of a chart by its name. Assume that the name of our chart is “Chart 1”. Then we can find the style number of the chart using the following simple VBA macro.
Dim MyChart As Chart
Set MyChart = ActiveSheet.Shapes("Chart 1").Chart
Debug.Print MyChart.ChartStyle
End Sub
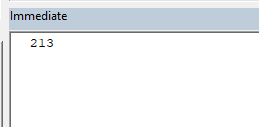
If we run the above macro the style number of the Excel chart will be printed in the immediate window like this.
In this next example you will learn how to go through all the charts in the worksheet and print their names and style numbers. Here is the example sheet I’m going to use.
Let’s name this subroutine as FindChartStyleNo_AllCharts
End Sub
We need two variables for this subroutine.
Dim Sh As Shape
Next we can assign the worksheet to the WS variable as follows.
Now we need to iterate through all the shapes of the worksheet. We can use For Each statement to do that.
Next
Inside the For Each loop we need to separate only the charts. Because lots of other objects also belong to this shapes collection. So here we are going to use an If statement and the “Shape.Name” property to distinguish charts from other objects. Once charts are extracted then we can print the name and the style number in the immediate window.
Debug.Print "Chart name - "; Sh.Name & " Style Number - " & Sh.Chart.ChartStyle
End If
So here is the full code of this subroutine.
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim Sh As Shape
Set WS = Worksheets("Sales data")
For Each Sh In WS.Shapes
If InStr(1, Sh.Name, "Chart", vbTextCompare) > 0 Then
Debug.Print "Chart name - "; Sh.Name & " Style Number - " & Sh.Chart.ChartStyle
End If
Next
End Sub
This is the result of the above subroutine
But this method will only work when the user hasn't changed the chart name manually. If it is possible for the user to change the chart names then you can use the “Shapes.Type” property instead of the “Shapes.Name”. This is how you can modify the If statement section to use “Shapes.Type” property.
Debug.Print "Chart type - "; Sh.Type & " Style Number - " & Sh.Chart.ChartStyle
End If
3 is the MsoShapeType value that represents the charts. Check below article from Microsoft documentation to see the values for different types of shapes.
MsoShapeType enumeration (Office)