Function is a block of code which can be used multiple times inside a program. So you can omit writing the same code again and again by using functions. Also programmers can break down the problem into smaller segments by using the functions. This will help programmers to organize their codes in a more meaningful way. Functions normally return a value to the sub or to the function called them. So in this lesson you will learn how to return a string from a VBA function. Here is the syntax of a function which returns a string.
Function FunctionName() as string
'-----------------------
'Codes of the function
'-----------------------
FunctionName = ResultString
End Function
Above is the syntax of a function which has no arguments. So let’s create a very simple function which outputs a string using the above syntax.
WebsiteName = "Excel-VBA Solutions"
End Function
Above function returns the name of this website whenever it is called. Now you can call this function from a subroutine or from another function. This is how you can call the above function from a subroutine.
Dim Response As String
Response = WebsiteName()
Debug.Print Response
End Sub
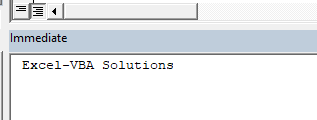
When you run the subroutine, the name of the website will be printed in the immediate window.
Next let’s look at how to develop a function which has an argument. Here is the syntax of a function having one argument.
Function FunctionName (Argument as type) as string
'-----------------------
'Codes of the function
'-----------------------
FunctionName = ResultString
End Function
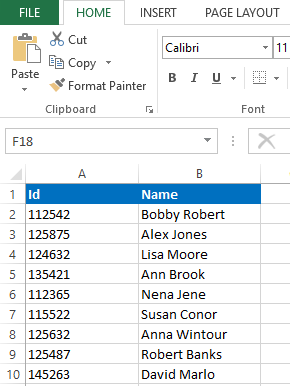
Type of the argument doesn’t need to be a string type. You can pass an argument of types such as Integer, Long, Boolean, Variant etc as well. Next let’s see how we can develop a function with an argument which returns a string. This is the sample Excel sheet I’m going to use for this example.
For this example I’m going to create a function which can return the employee name when we pass Id as the argument. Let’s name this new function as FindName. We need to use a For Next statement inside our function to get the expected result. Assume the name of the worksheet is Data. You can develop the function as below to get the name of the employee when passing the Id as argument.
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim i As Integer
Dim LastRow As Integer
Set WS = Worksheets("Data")
LastRow = WS.Cells.Find("*", [A1], , , xlByRows, xlPrevious).Row
For i = 2 To LastRow
If WS.Range("A" & i).Value = Id_no Then
FindName = WS.Range("B" & i).Value
Exit Function
End If
Next i
'If id not found
FindName = ""
End Function
So above is an example VBA function with an argument which returns a string. Program check for the matching id while iterating through each row number. If it finds a matching id then the function will return the corresponding name. Exit function statement is used to stop executing other lines of code once a function finds a match. If the Id is not found, the function will be executed til the end and will return an empty string. Here is how you can use the above function inside a subroutine.
Dim EmployeeName As String
Dim IdNumber As Long
IdNumber = 135421
EmployeeName = FindName(IdNumber)
MsgBox EmployeeName
End Sub
Name of the relevant employee will be displayed in a message box when the code is executed.
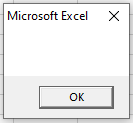
This is what happens when you pass an Id which is not available in the worksheet.
Dim EmployeeName As String
Dim IdNumber As Long
IdNumber = 135429
EmployeeName = FindName(IdNumber)
MsgBox EmployeeName
End Sub